Weavonic
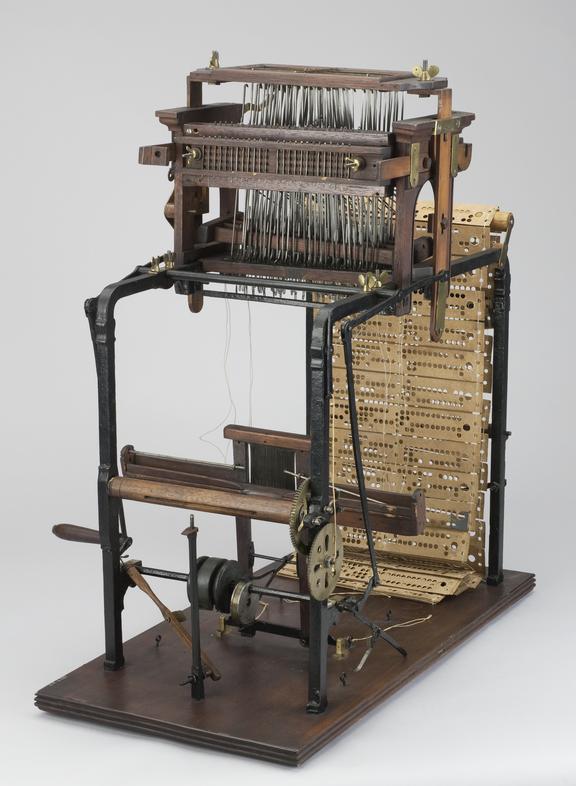
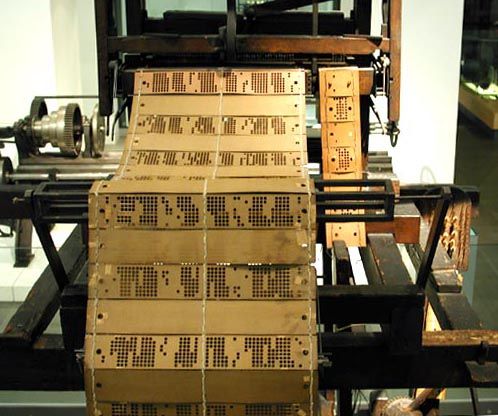
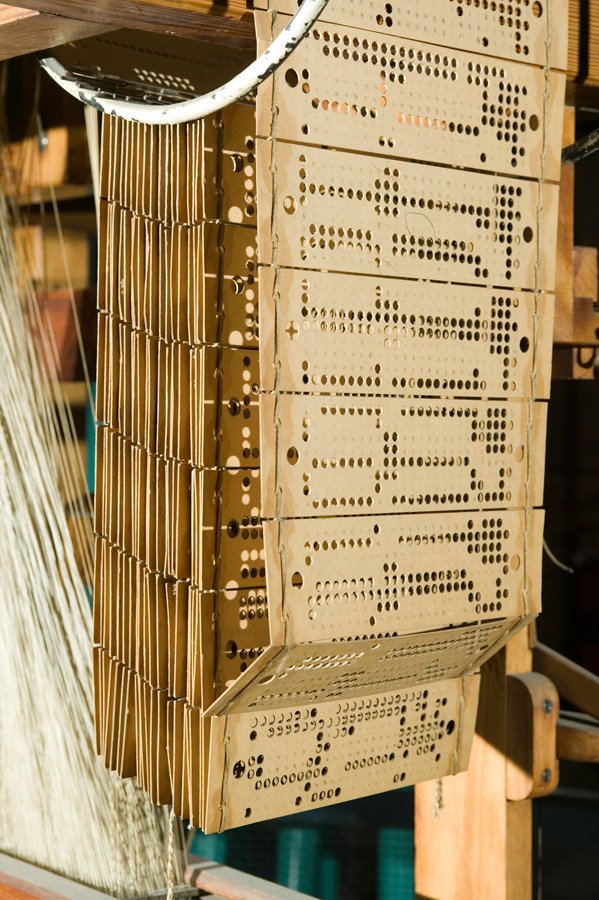
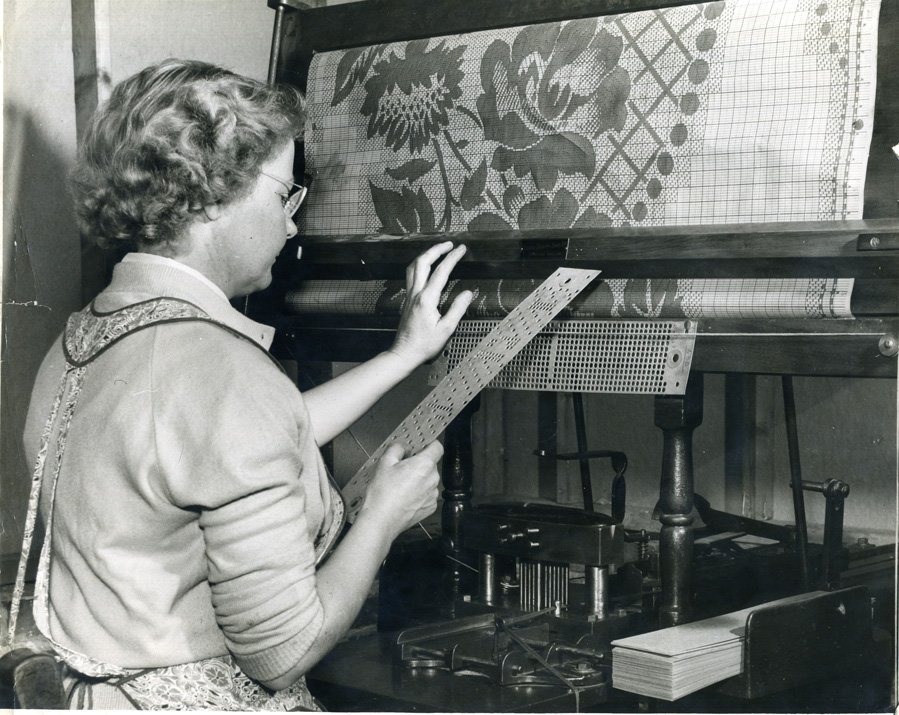
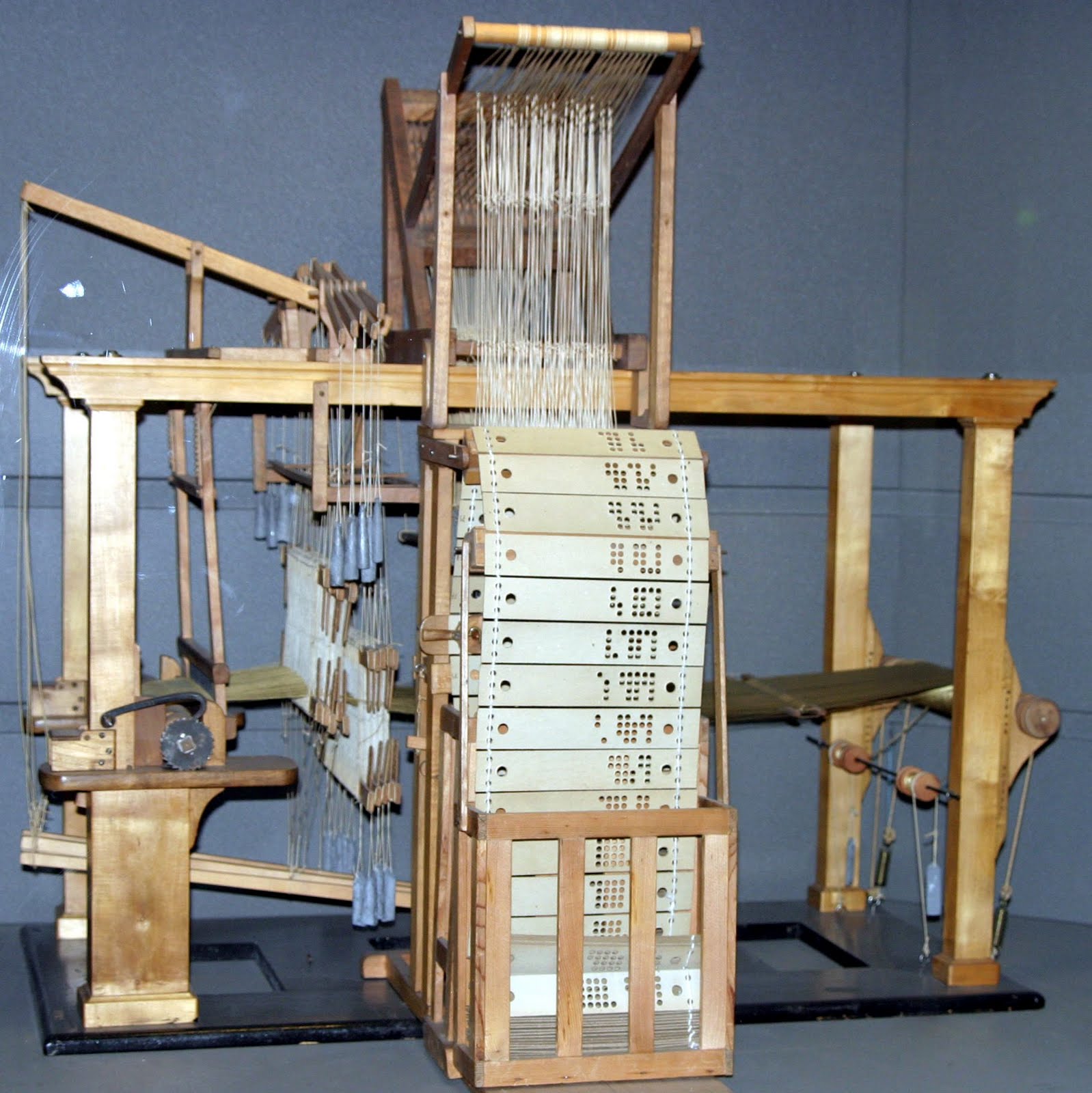
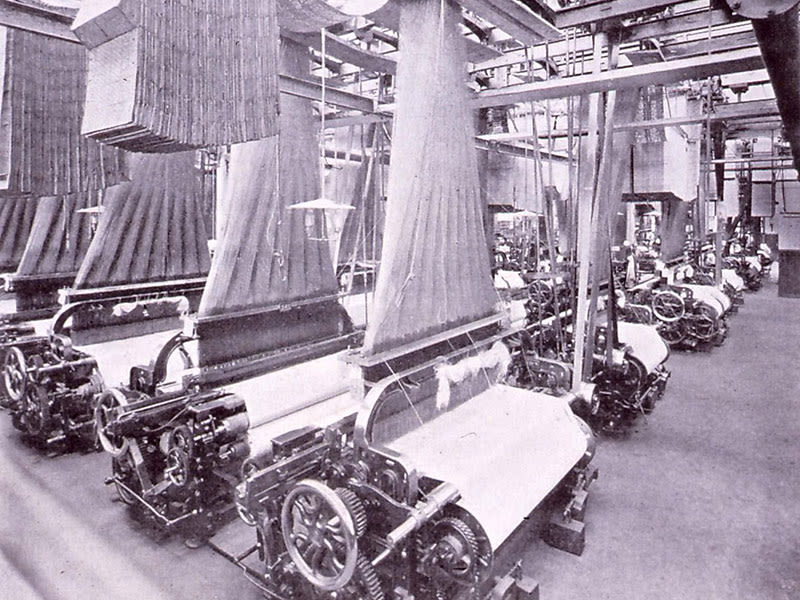
Weavonic is a state-of-the-art mobile application designed to transform the textile design process by digitizing traditional punched cards. The app uses mobile camera to capture high-resolution images of the punched cards, which are then processed using an image processing algorithm. This algorithm extract detailed patterns from the images and convert them into bitmap files. These bitmaps can be used as digital punched cards for modern electronic Jacquard looms, thus bridging the gap between historical and contemporary textile manufacturing methods.
The application’s architecture incorporates several key technologies to achieve this transformation. It utilizes the mobile camera for image capture, ensuring high-quality input for accurate design extraction. The image processing is handled by advanced algorithms, often leveraging libraries like OpenCV to decode and interpret the card patterns. Once processed, the designs are converted into bitmap files that can be seamlessly integrated with electronic looms. For secure storage and file management, the app employs cloud storage solutions, and it uses the Android SDK for developing the mobile application interface. Additionally, Chaquopy is used to enable Python integration for complex processing tasks, while the Google Drive API facilitates cloud storage and file access. Together, these technologies enable Weavonic to modernize the textile design process by turning traditional punched card data into a digital format that can be used with contemporary weaving technology.